LOOM Price Analysis:
The Loom Network is a next generation blockchain platform designed to allow large scale applications to be launched on the Ethereum blockchain. It is the first production-ready solution capable of increasing the core capacity of Ethereum. The Loom Network launched in March 2018, well ahead of higher-profile scaling solutions like the Raiden Network and Plasma. Its first target market is blockchain based collectibles in the gaming market. The LOOM token is designed to be an all-access membership token that gives users access to Dapps and network operations that run on the Loom Network.
The price of the Loom-token (LOOM) has fallen by 1% in the last month and is currently trading at ~USD 0.07. Over the same period the total crypto market cap has risen ~33%. The project has recently implemented a number of significant updates including an upgrade to the network’s Delegated-Proof-of-Stake consensus model in late May. It has not caught the wave of positive buying momentum permeating through the crypto markets over the last month. It currently occupies the 110th position on Brave New Coin’s market cap table.
The Loom Network has gained attention because of its implementation in a key industry use case, blockchain based gaming. The Ethereum blockchain supports the creation of NFTs, or non-fungible tokens (ERC-721 protocol). These are non-identical, unique blockchain assets that function differently from other crypto assets. 1 ETH or 1 LOOM can easily be interchanged for another ETH or LOOM. However, 1 CryptoKitty, an NFT, cannot be replaced with another CryptoKitty, because each CryptoKitty is defined by a unique set of characteristics despite being an asset within the same domain.
This unique property allows games based around collectibles, like trading cards, to be hosted on the blockchain. Blockchain-based in-game collectible purchases don’t require a central party, which makes them easily trackable, and more liquid. However, this also means that every in-game transaction will incur gas fees, making gaming sessions expensive. Additionally, games played using browsers like Metamask, will require signatures on every transaction, making for cumbersome UX.
The Loom Network offers blockchain gaming projects an early, production-ready version of an Ethereum scaling solution based on Plasma. Notable NFT based games like Axie Infinity and a number of LOOM Software Developer Kit (SDK) community built games like Neon District, Crypto Wars and Battle Racers are utilizing the LOOM scaling solution. These games can offer blockchain based benefits but at a cheaper cost and higher capacity.
The Loom SDK natively supports non-fungible ERC721/ERC721x tokens and allows data such as wins, losses, and participation, to be recorded off the Ethereum main chain without incurring gas costs.
The Loom team has discussed the project’s focus on building strong UX solutions for consumer-focused gaming and social media Dapps by providing a seamless transaction experience. The Axie Infinity deal fits well into this characterization.
Source: nonfungible.com, daily onchain transaction volume for Axie infinity
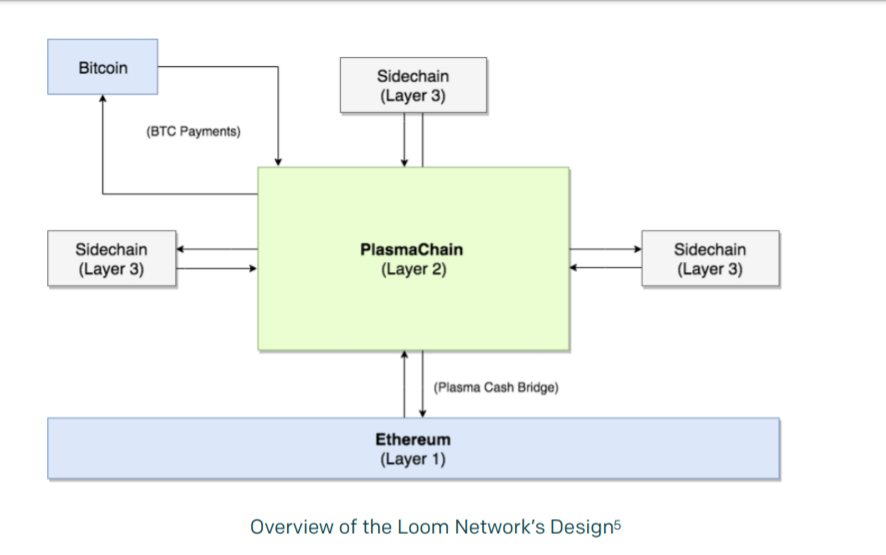
The Loom Network has built a core mainnet Plasma-based chain called PlasmaChain (formerly known as Zombiechain) a DPoS based chain which Dapps can deploy on to increase scaling capabilities. Developers have the option to build their own, native Dappchains using the Loom Network.
PlasmaChain is the first domain-specific project (Ethereum) to be built by LOOM. In the future LOOM will build side chains for other platform blockchains using Tendermint powered consensus. The Loom Network has cross-chain capability, and building interoperability with other major platform blockchains like Tron and EOS appears to be a key goal for the project in 2019. In the future, Loom hopes to build the universal layer-2 solution that caters to Dapps across the ecosystem.
Plasma works by using smart contracts that act as child versions/Layer 2's of the root or parent or Layer 1 chain (Ethereum in this case). These handle the bulk of transaction operations before final verification (and mining) occurs on the main chain. Plasma child chains can have their own tokens to reward/incentivize validators. Bad actors can immediately be caught by asking for transaction confirmation of child chain operations from the root chain.
Note: Loom Network runs using Plasma cash as opposed to Plasma MVP
Loom is a network of side chains connected through the central PlasmaChain. The PlasmaChain is maintained by external node validators (such as Chorus One) and utilizes Tendermint-powered Proof-of-Stake consensus (which utilizes the LOOM token as staking medium). Applications and games can run on connected third layer sidechains/networks that can be managed by various parties such as game development houses.
The Loom PlasmaChain: Current centre of the ecosystem
The Loom PlasmaChain is the first implementation of a Loom domain specific Plasma solution. It functions as a high-performance DPoS layer 2 chain that acts as a bridge between multiple chains and Ethereum and acts as the core of the current LOOM token staking model. It can support smart contracts and proposes to offer faster transaction times and more capacity than Ethereum. It operates with a unique set of block validators who are guaranteed to be assigned to blocks and are paid out for their services through tokens held by the LOOM treasury.
LOOM tokens must be staked in large amounts in order to become a validator node on a LOOM DPoS Dappchain, and in order to elect these validators, users need to stake tokens for voting rights.
LOOM token holders can also choose to be delegators, in order to do so they temporarily relinquish their LOOM tokens and freeze them into a smart contract. Any LOOM holder can become a delegate and assign their tokens to a node validator. Validators charge a small fee to cover hardware and set-up costs.
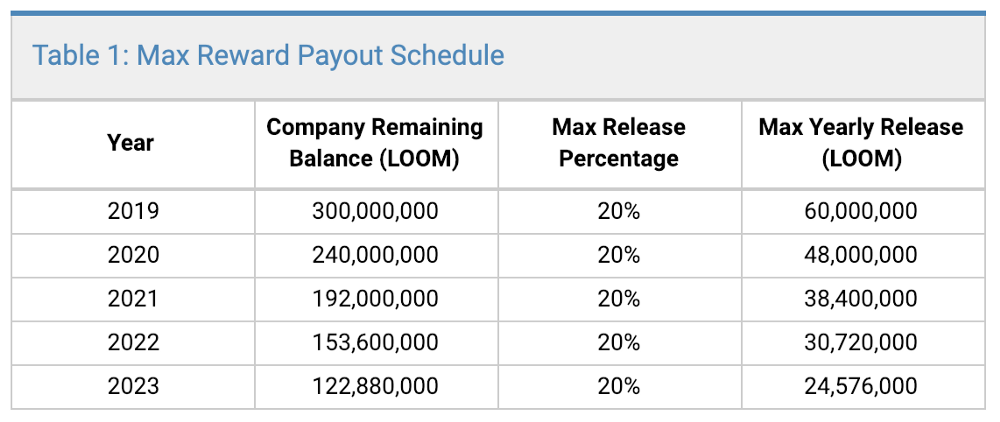
From the total supply of LOOM, 300 million tokens or 30% of supply has been set aside for staking rewards by Loom network operators. A maximum of 20% of the staking reward allocation can be distributed each year. This means that over time the block rewards paid to stakers will decline year on year as the staking reward pool drops.
Since 300 million LOOM tokens have been allocated to network stakers over time at a reducing rate, staking rewards from block rewards also reduce over time. The other factors affecting the rate at which staking rewards change include; Length of lockup period- holders choosing to lock their LOOM for longer periods earn more, interest in LOOM staking- more stakers means allocation caps are hit more quickly, fees charged by PlasmaChain Dapps which is partially paid to stakers, validator commission rates charged to delegates which may change based on infrastructure requirements and network congestion.
A more unlikely factor is validator slashing. If a node attacks the network or is offline for an extended period of time, this can lead to the destruction of both the validators and its delegators stake to the network. Slashing conditions for LOOM holders were defined more clearly as part of the DPoS 3.0 update.
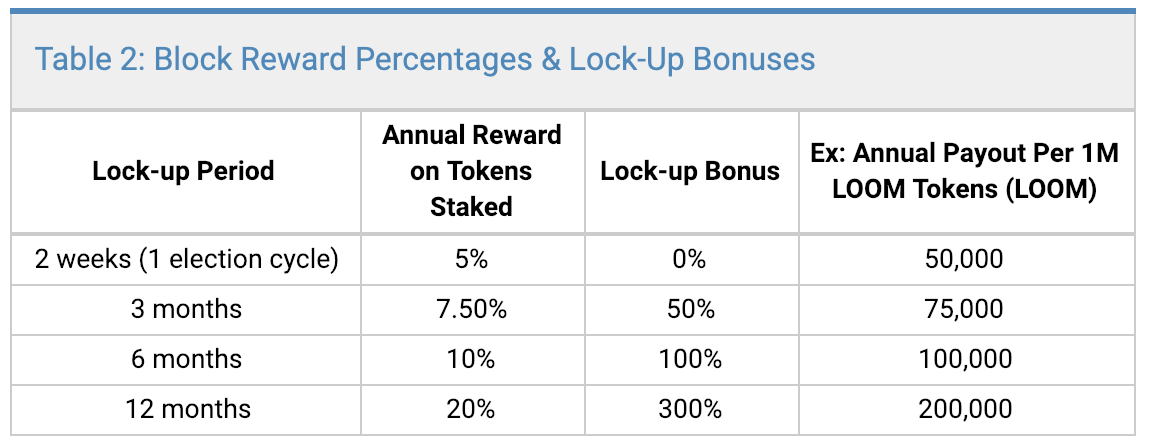
Delegated proof of stake networks are stronger and more secure as more circulating tokens are staked. Loom has incentivized holders to lock up as money tokens as they can for long periods, given the diminishing reward schedule and lock-up bonuses (LOOM staking on the PlasmaChain for a year earns 300% more annually than a user who doesn’t stake at all.)
In late May 2019, the Loom Network launched an upgraded version of PlasmaChain DPoS. Loom staking rewards are now automatically compounded, meaning newly awarded LOOM is instantly restaked and earns 5%. Delegators can now assign tokens to multiple validators with different lock-up periods, this was previously not possible. Other details surrounding the v3.0 update can be found here.
The Loom network target market: Developers and users
A key demand driver for LOOM is the number of game creators and studios deciding to launch applications using PlasmaChain. Running an application utilizing Loom requires the creator to lock a large amount of LOOM to the network. In a model analogous to the EOS network, app operators are charged ‘bandwidth’ fees every month proportional to the amount of transactions per second their app users consume and these fees are paid to validators.
For users, LOOM can be used for in-Dapp purchases, for example, the Loom powered Zombiebattleground game lets users sign up for 'game membership' using LOOM and gain access to free game cards every month. Users are required to hold at least one LOOM token when interacting with LOOM dapps to enable them to move assets back and forth to the main Ethereum network.
As mentioned earlier, currently the value of the LOOM token depends on the stability of the PlasmaChain. LOOM’s value will increase if more Dapps choose to build on top of the PlasmaChain and demand tokens to pay for bandwidth, if delegates choose to lock up tokens for longer periods, and if there is more demand to become a network validator due to higher rewards. LOOM will lose value if holders lose interest in staking because of factors like frustrating UX and node validators being slashers.
As per the 2019 roadmap released on April 19, since the staking of LOOM tokens was launched in February 2019, in two months users staked 149,363,113 tokens, representing over 20% of the circulating supply and $10,000,000+ USD in value. The PlasmaChain launched with 15 validators but this number is likely to expand.
In the roadmap, Loom outlines 4 key goals for ecosystem development in the next year. Incentivizing staking by LOOM holders, and increase end-user adoption of the PlasmaChain (more gamers, more daily active users and more value locked on-chain). Thirdly, create more transaction fee avenues to incentivize more delegates, and finally, validate participation and interoperability with other platform blockchain users.
To meet these goals over the next year the Loom Network plans to grow the ecosystem, through initiatives like:
- New dashboards for wallets and browsers that simplify UX processes when staking.
- Encouraging the development of more games like Relentless which have crisp UI and straightforward onboarding to garner more mainstream interest in blockchain gaming.
- Encouraging Dapp building through improved developer documentation and programs like Crypto Zombies.
The Loom Network also operates Crypto Zombies, one of the world's most popular Ethereum coding schools. The platform helps developers learn the basics of Solidity and SolidityX and eventually teaches them how to deploy Dappchains within the Loom network. Crypto Zombies has users in over 200 countries with meetups in places such as Tokyo, Sydney and Tegucigalpa, Honduras.
Crypto Zombies aims to encourage the first wave of Loom Network Dapps, while also growing the wider Ethereum ecosystem. To investors and retail traders, it is a sign that the Loom Network is at the forefront of Ethereum Dapp development and may create some underlying buying pressure for LOOM.
Source: Stateofthedapps.com
Dapp aggregator State of the Dapps tracks the Loom Network Ethereum mainnet smart contract as a singular Dapp. Data suggests there has been steady growth in the number of active users and transactions on the network over the course of the last month. The Loom Network has averaged ~180 transactions a day over the last month across ~57 active users.
Objective on-chain indicators
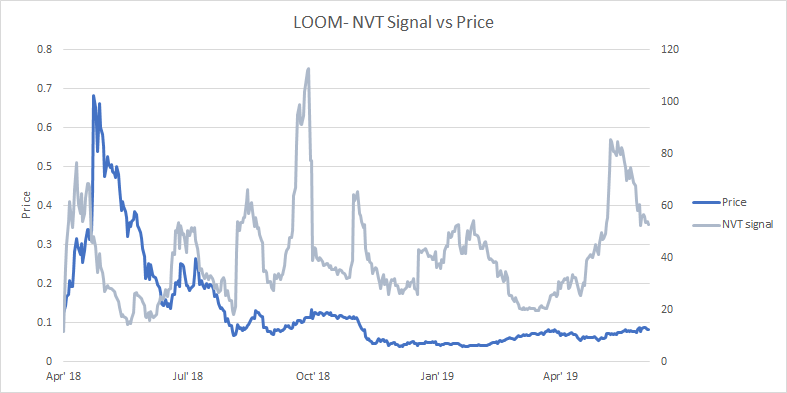
NVT Signal
Derived from the NVT ratio, the NVT signal is a responsive blockchain valuation metric developed by Willy Woo and Dmitry Kalichkin.
Crypto markets are prone to bubbles of speculative purchasing that don’t reflect underlying network fundamentals. The NVT signal provides insight into what stage of this price cycle a token may be at.
A high NVT signal is indicative of a network that is going through one of these bubble periods and may move towards a position of becoming overbought/overvalued, as the market's speculative momentum slows.
Data sources: Brave New Coin, Coinmetrics.io
In the past, periods of sharply rising NVTS have often preceded periods of rising LOOM value, particularly when NVTS approaches the 60 point level and clearly hits a point of being ‘oversold’ based on fundamentals.
In the short term, fundamental signals lean bearish given the LOOM NVTS is presently falling sharply after hitting an inflection point in May 2019. This suggests there is currently downward fundamental price pressure that may soon be reflected in token value. A price pullback of LOOM may be incoming.
However, LOOM is still a new project with key fundamental value drivers like token staking protocols on the PlasmaChain only launched in February 2019. The falling NVT signal has coincided with the recent price run of LOOM, this means on-chain volume is rising more quickly than the token's market cap/value.
This pattern suggests that the period of rising external value is being backed by tangible economic activity. Because of LOOM’s emerging value proposition as a store-of-value token designed not to be transacted frequently, the relationship between LOOM’s NVTS and external value may be changing.
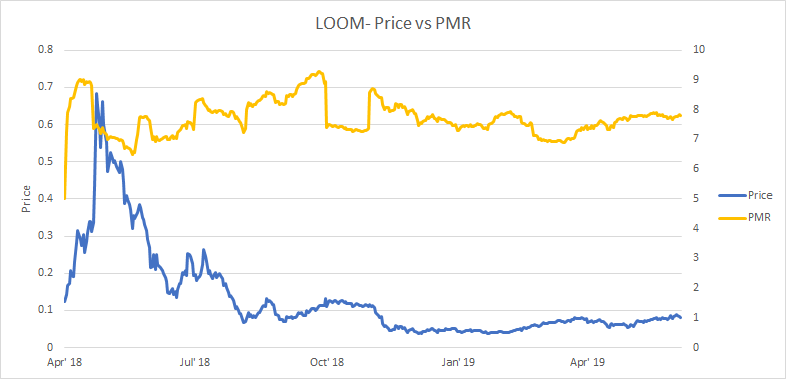
PMR
Metcalfe's law is a measure of the connections in a network, as established by Robert Metcalfe, the founder of Ethernet. It has subsequently been used to analyze the true value of network-based financial products like Facebook and Bitcoin. By comparing it to price, it can provide a useful tool to assess whether a token is over or undervalued.
It is also a more straightforward metric to assess when compared to on-chain transaction volume, which can be challenging to measure accurately in USD terms. Addresses are measured as the number of unique sending and receiving addresses participating in transactions daily.
Data sources: Brave New Coin, Coinmetrics.io
The PMR for the LOOM network has been historically high and has hovered between 7-9 natural log points since early 2018. This implies that the token value dominates vs number of active addresses of LOOM and that the token derives little value from wider community effects at this early stage. This suggests that most of the token’s value is speculative and derived from an assessment of future value.
A cryptocurrency’s network effects increase when new users join and strengthen the network, making it more valuable for existing users. The most direct network effects are improved liquidity and utility. More daily active users can be indicative of a higher level of game adoption developer adoption from Loom network (more places to spend LOOM in-app) and more counterparties willing to accept LOOM for payments or sell their stake to.
Exchanges and trading pairs
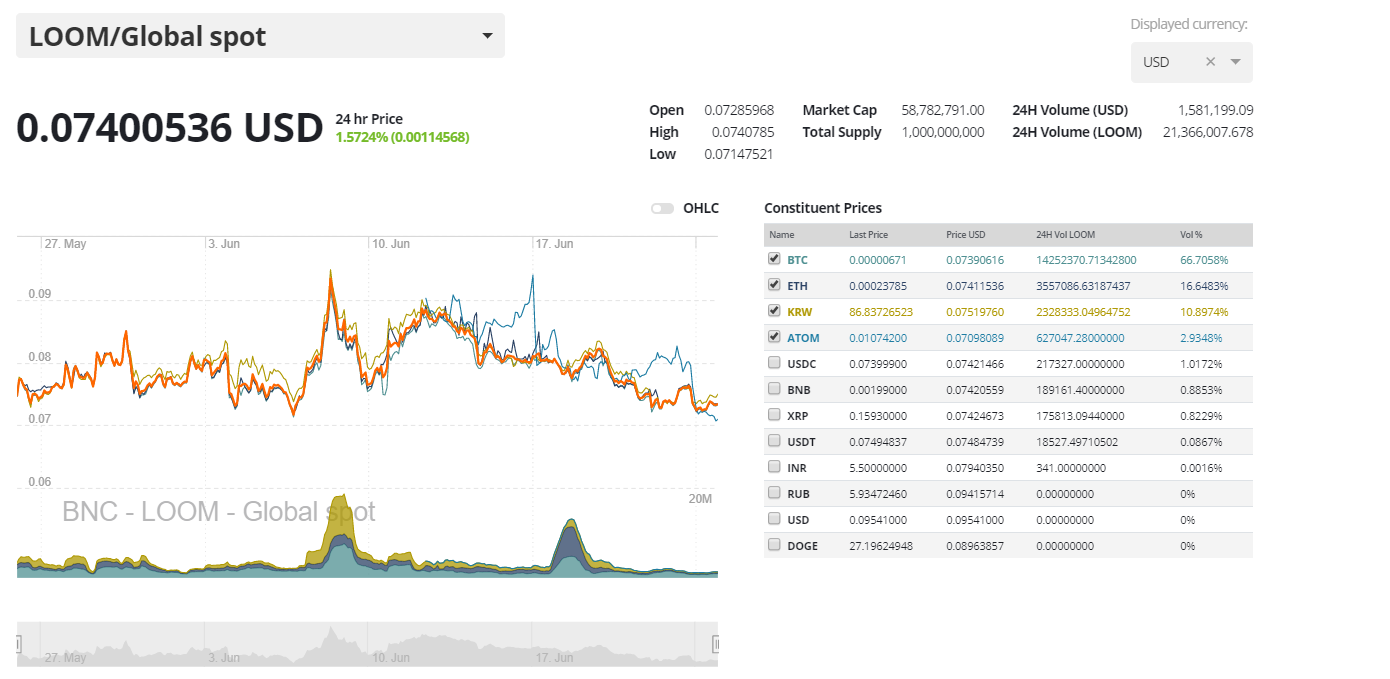
The most popular trading option for LOOM is BTC with the pair currently handling close to 67% of daily trading volumes. The second most popular market is the LOOM/ETH pair. Together the top two pairs make up over ~83% of the daily trading volume. The Korean Won pair is the most popular fiat off-ramp liquidity solution for LOOM. Over the last month, there have been short term spikes in both ETH and Korean Won trading volumes.
The USD value of the daily volume of the entire LOOM trading market is ~USD 1.576 million.
A mix of exchanges contributes to the LOOM trading ecosystem, with the top 5 pairs spread across 5 exchanges. The LOOM/BTC market on Coinbene is the most active market in the ecosystem. LOOM is also tradeable on high profile exchanges such as Binance and Bittrex.
Technical analysis
Moving Averages and Price Momentum
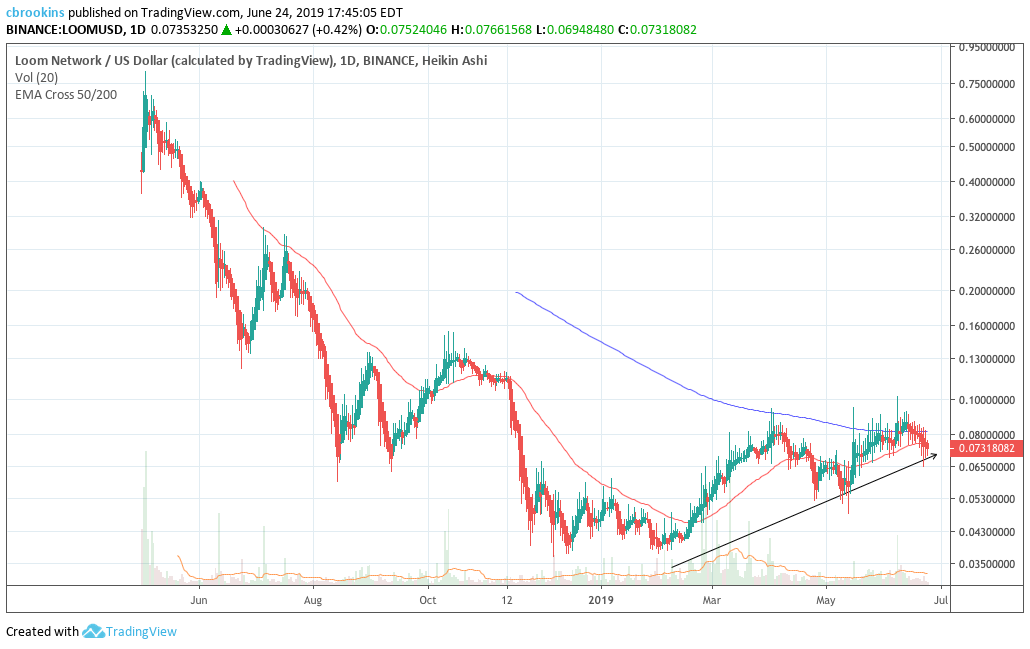
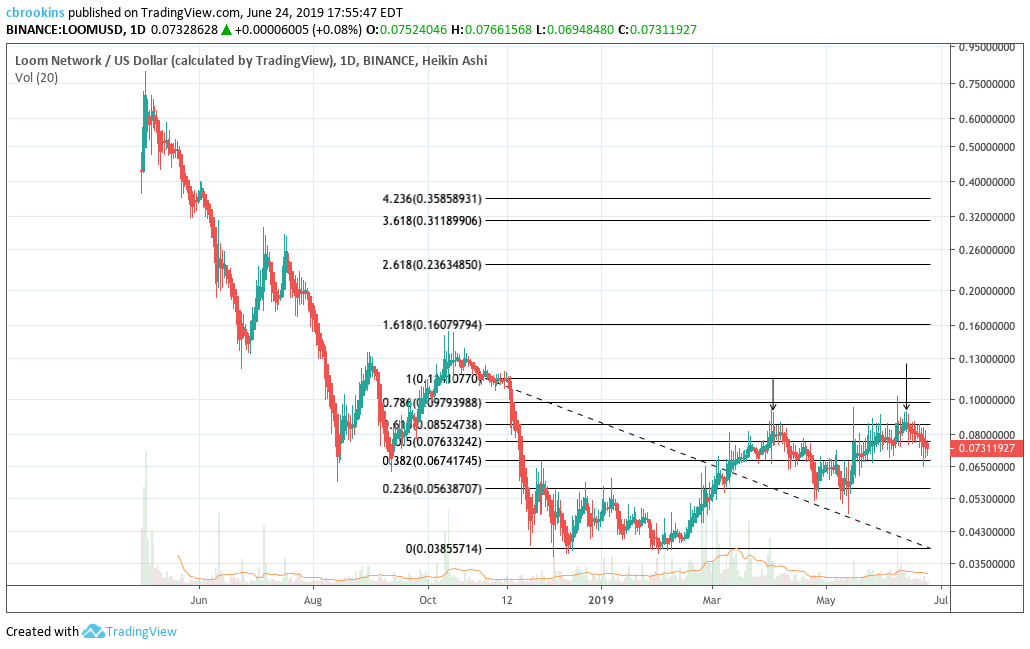
On the 1D chart, a golden cross has yet to occur for LOOM despite following a strong linear trend in 2019, which has resulted in an 87% price increase. Despite the lack of golden cross, price has consistently used the 50 day EMA as support. However, price is currently slightly beneath the 50 day EMA. If the 50 day EMA support fails, coupled with the linear trend (price falling through the arrow), that would be a sell signal to traders.
On the 1D chart, LOOM’s 2019 price patterns have generally followed the Fibonacci retracement levels. Particularly, price has failed to break above the 0.618 level of $0.085. Currently, price is beneath the 0.5 Fibonacci level and trending towards the 0.382 Fibonacci level of $0.067. If so, it is critical for price to hold that level or risk falling further to 0.236 ($0.056)
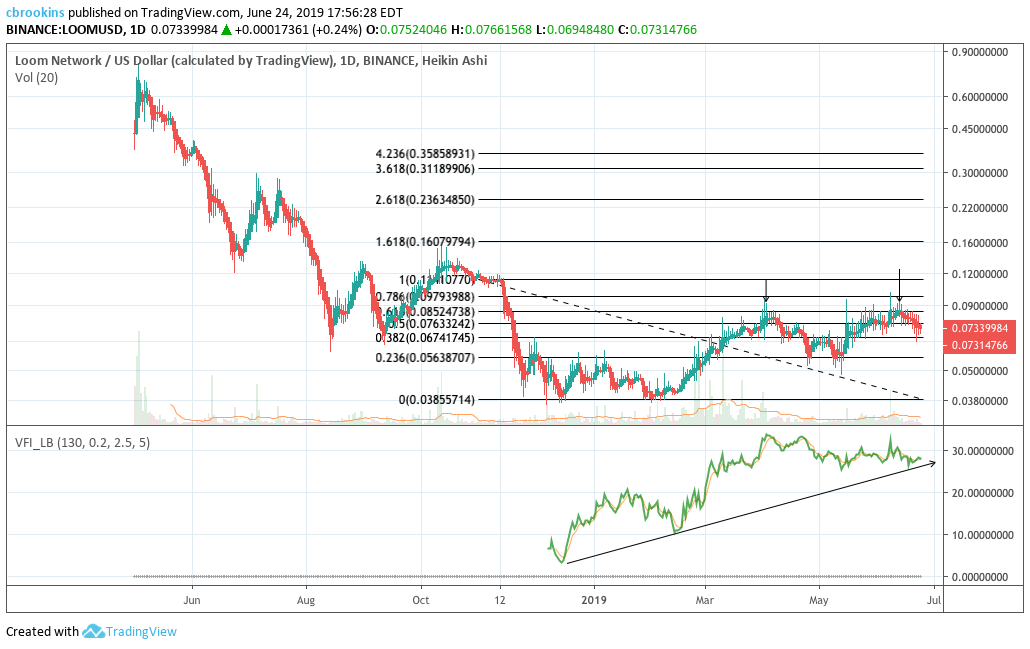
Lastly, on the 1D chart, the volume flow indicator (VFI) is still well above 0 and following a strong linear trend. If price falls through the trendline that would likely signal demonstrable price weakness ahead. However, the linear trend remaining intact provides a bullish outlook for LOOM despite the current weakness.
Ichimoku Clouds with Relative Strength Indicator (RSI)
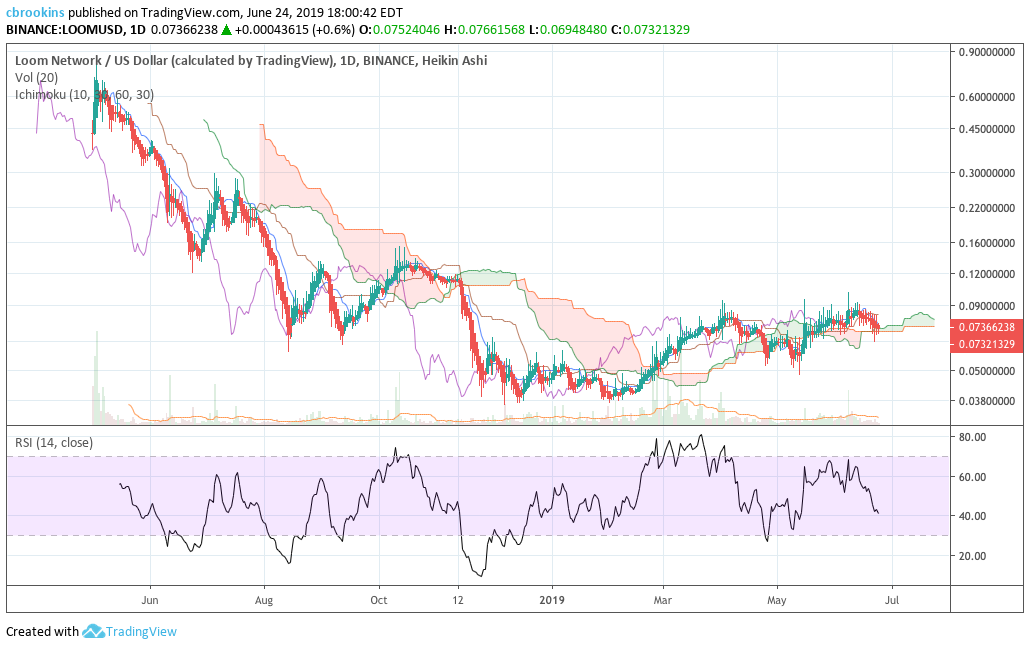
The Ichimoku Cloud uses four metrics to determine if a trend exists; the current price in relation to the Cloud, the color of the Cloud (red for bearish, green for bullish), the Tenkan (T) and Kijun (K) cross, Lagging Span (Chikou), and Senkou Span (A & B).
The status of the current Cloud metrics on the 1D frame with singled settings (10/30/60/30) for quicker signals are mixed: price is touching the Cloud, Cloud is bullish, the TK cross is bearish, and the Lagging Span is above Cloud and touching price.
A traditional long entry would occur with a price break above the Cloud, known as a Kumo breakout, with price holding above the Cloud. From there, the trader would use either the Tenkan, Kijun, or Senkou A as their trailing stop.
LOOM completed a Kumo breakout in early June, but has struggled to maintain it ever since. Price retested Cloud support of $0.071 three times already. Currently, price is slightly above this level with each previous retest making higher lows. If the breakout holds, price targets are $0.078 and $0.087. If price falters, support levels are $0.07 and $0.065.
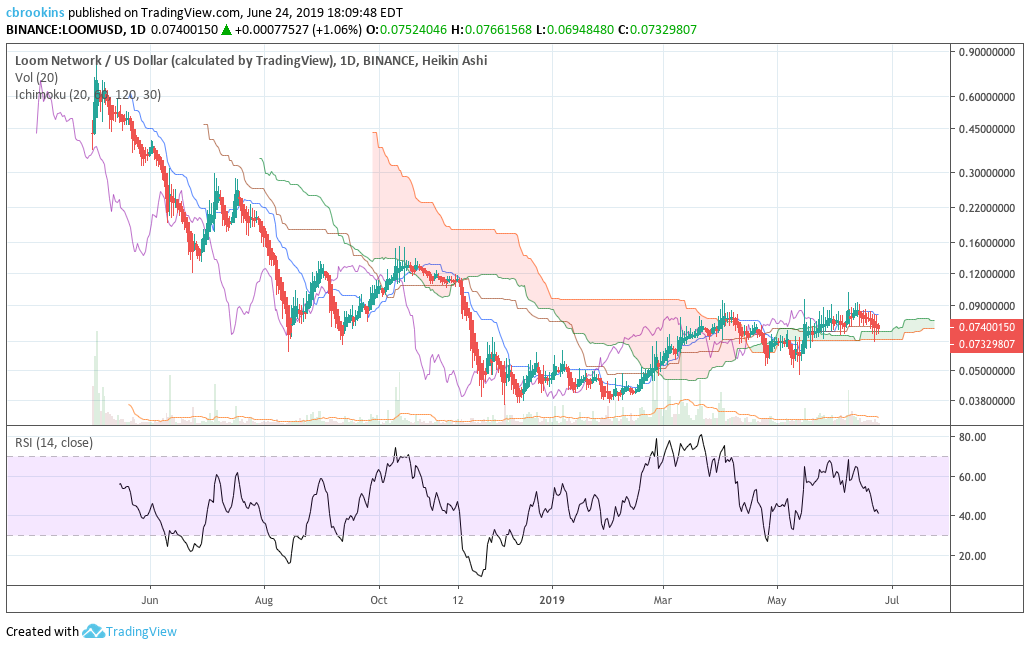
The status of the current Cloud metrics on the 1D time frame with doubled settings (20/60/120/30) for more accurate signals are mixed: price is above the Cloud, Cloud is bullish, the TK cross is bullish, and the Lagging Span is above the Cloud and touching price.
The slower settings yield very similar results; including current Kumo breakout, and price targets and support levels. However, the bounce off of Cloud support looks even stronger on the slower settings, especially when combined with the RSI nearing oversold territory.
Conclusion
The Loom Network is the first production-ready Ethereum Dapp scaling solution to utilize Plasma. It’s first targeted use-case, blockchain based collectible gaming, appears to be an excellent fit for the product. Games fitted with Loom Network scaling have already been launched on Ethereum.
Staking on the PlasmaChain provides a useful, stable way to earn passive income on held LOOM. The token’s new store-of-value proposition may help keep LOOM within the ecosystem and create long term investment value.
There are some concerns regarding the validity of DPoS based blockchain solutions. For example, bad actor node validators slashing the value of the network is a significant long term risk. As the nascent Loom project grows and more fundamental data is collected, its value and effectiveness as a scaling solution for platform blockchains should become more clear.
The technicals for LOOM are currently sending mixed messages. Despite the current Kumo breakout, a conservative approach for both the fast-setting trader (10/30/60/30) and slow-setting trader (20/60/120/30) would be to await price to firmly hold its breakout above $0.073 before entering a long position. If the aforementioned occurs, price targets are $0.078 and $0.087. If the breakout falters, support levels are $0.07 and $0.065.
OhNoCrypto via https://www.ohnocrypto.com/ @Aditya Das, @Khareem Sudlow