Bitcoin Price Analysis - Global markets ablaze
Bitcoin (BTC) is a decentralized digital currency released by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009, shortly after the Global Financial Crisis. The market cap is currently US$107.55 billion, with US$13.48 billion traded in the past 24 hours. The current spot price is down 72% from the all-time high established in December 2017 and down nearly 46% in the past month. All crypto assets have suffered over 30% declines over the past week.
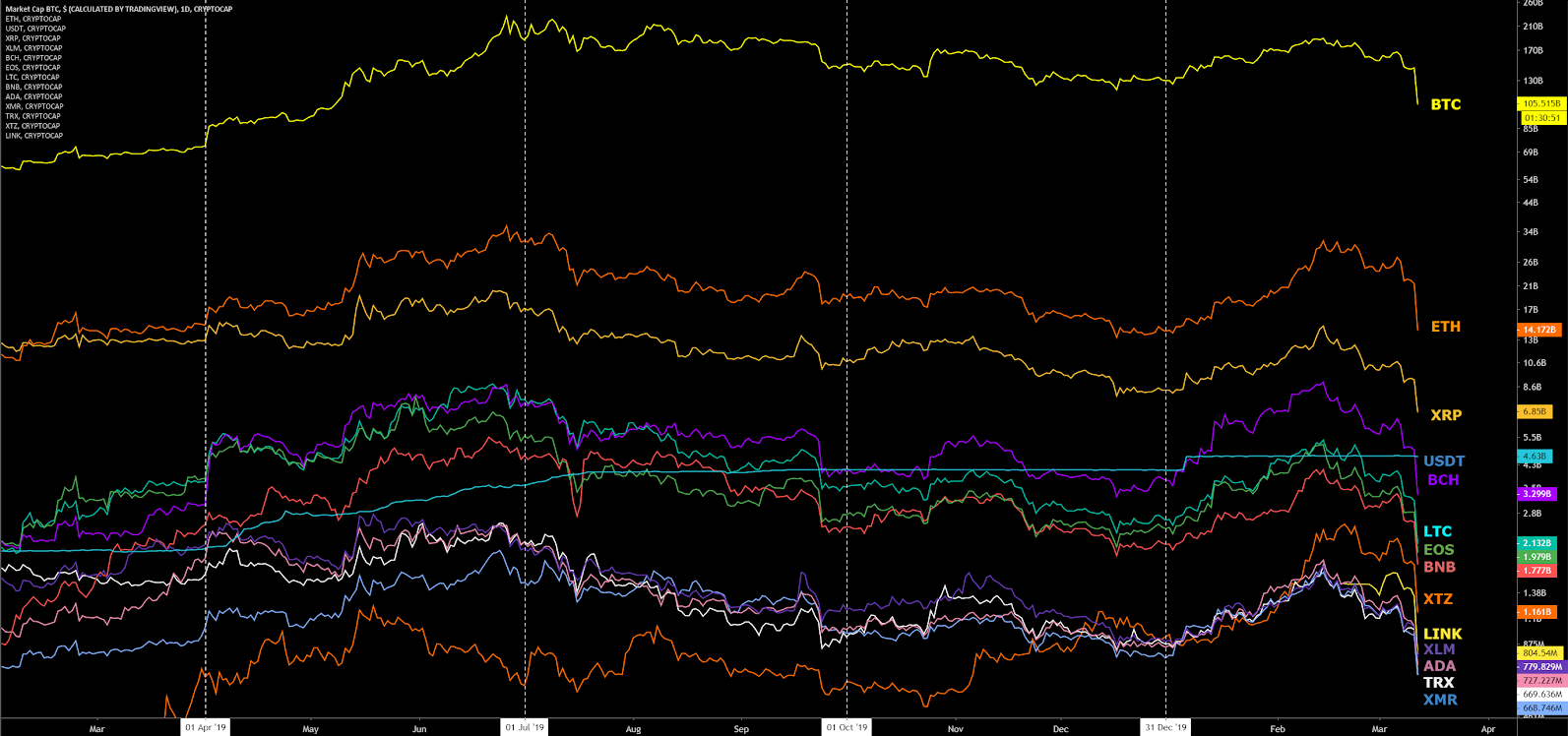
The BTC network is secured by the SHA-256 consensus algorithm. Both the network hash rate and network difficulty repeatedly posted record highs in 2019 and 2020. The increases were likely due to both new ASICs being manufactured as well as relatively cheap electricity available in China, and elsewhere, enabling older ASICs to again become profitable.
As BTC spot prices began to decline later in the 2019, the hash rate increases slowed slightly, leading to a temporary and volatile hash rate plateau. If BTC spot prices continue to decline in 2020, more and more miners will likely turn off their ASICs or mining operation, until mining profitability increases.
Average block times are currently over 12 minutes, suggesting a projected decline in difficulty in the next two weeks. Network difficulty adjusts up to +/-25% every 2,016 blocks. As hash rate decreases before a difficulty adjustment, block times increase. As hash rate increases before a difficulty adjustment, block times decrease. The adjustment will target a 10 minute blocktime.
BTC inflation stands at 3.67% and is set to decrease in a stepwise fashion over time. The next block reward halving is estimated to be 88 days from now, around May 12th, when annual inflation will decrease to 1.80%. As miners add hash rate to the network, and maintain a block time less than 10 minutes, the estimated time until the next halving will continue to slowly decrease.
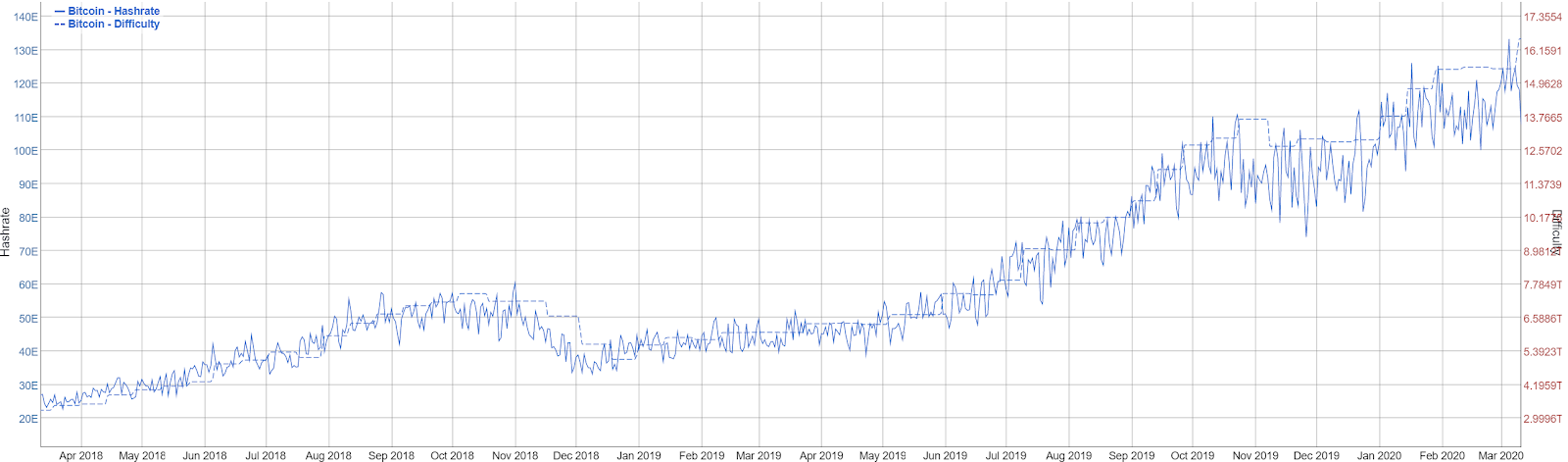
Twenty-three new SHA-256 ASICs were released in 2019, with two released by Bitmain in December. Four more ASICs are set to be released this year, which may explain the continued rise in hash rate in early 2020. The most profitable miners are currently the; Bitmain Antminer S17+ and 17e, ASICminer 8 Nano Pro, and the MicroBT Whatsminer M20S.
Renewable energy sources around the world, including hydroelectric and geothermal power, bring electricity prices for most mining farms to US$0.04 cents/KWh or lower. Currently, 37% of the SHA-256 ASICs are not profitable. If electricity prices suddenly rise or if BTC prices continue to drop, more and more ASICs become unprofitable and the hashrate will drop further.
Post-Halving, many of these ASICs will likely become unprofitable completely if price does not increase dramatically. Other network factors that influence mining profitability include; price, block times, difficulty, block reward, and transaction fees.
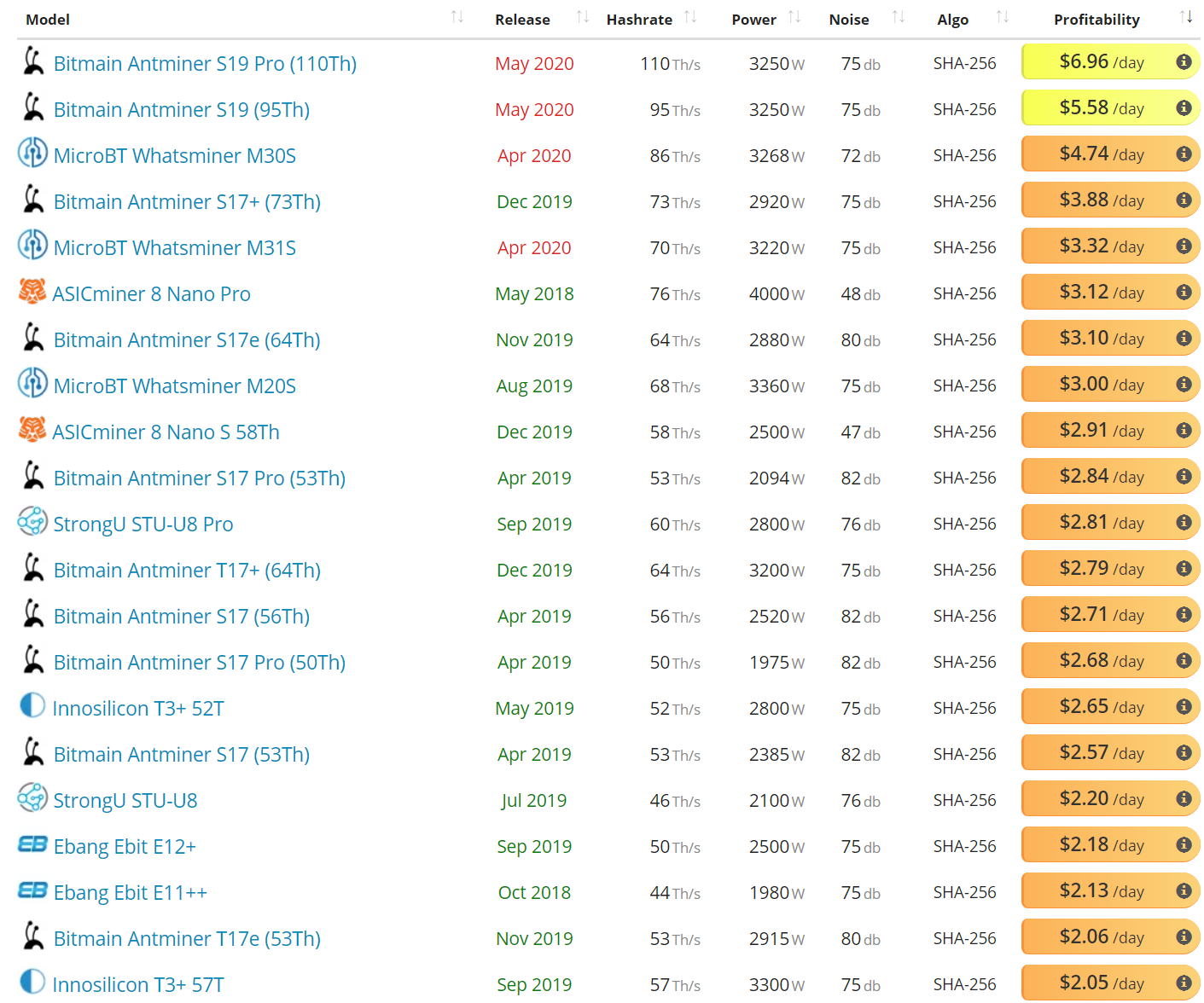
On the network side, both the on-chain transactions per day (line, chart below) and average transaction value in USD (fill, chart below) have risen significantly since April 2018 and February 2019, respectively. The current record for transactions in a single day was set in December 2017, at 500,000. The current record for average transaction values in USD was set on July 24th, at US$51,000.
Since July 2019, both of these metrics have declined, with transactions per day currently near 325,000 and the average transaction value at nearly US$9,300. Since the beginning of the year, both metrics have increased, with transactions per day up 10% and average transactions values up 50% over the past three months.
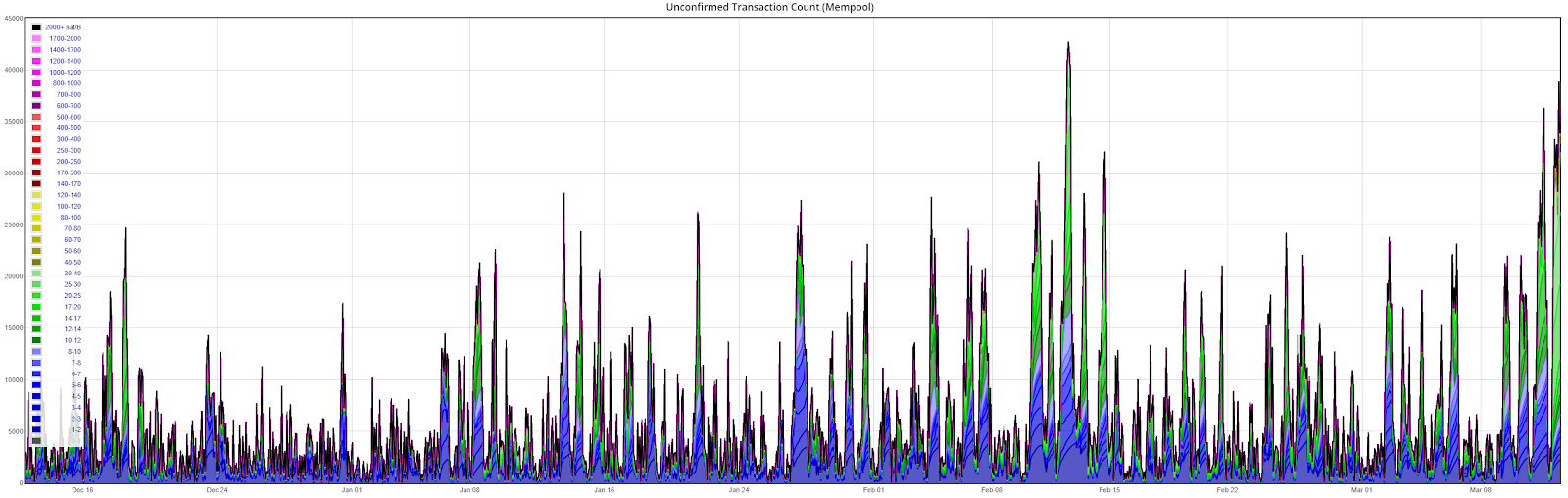
Unconfirmed transactions have mostly held below 20,000 since August 2019, during peak congestion, and have dropped below 5,000 during off-peak times (chart below). Over the past few days, with increased price volatility, unconfirmed transactions have increased to nearly 40,000 during peak times.
Since mid-July last year, unconfirmed transactions have only breached 35,000 on two other occasions; September 30, 2019 and February 12th, 2020. A decline in hash rate over the past few days is also a likely contributing factor to the current network congestion, as block times have now exceeded 12 minutes.
The average block size (fill, chart below) increased substantially from April 2018 to June 29th 2019, due to both an increase in on-chain activity as well as Veriblock (VBK), which secures other blockchains through the Proof of Proof consensus mechanism. From June 29th to late December, the average block size has dropped from nearly 4 MB to 1.35 MB. Since then, block size has increased to over 1.6 MB.
The average transaction fee (line, chart below) is currently US$0.63, despite a growing block size and increased on-chain use since the record high fee of US$62 in late December 2017. Both the lack of zero-fee unconfirmed transactions and increased scalability have kept fees substantially lower than late in 2017.
Additionally, transaction batching and the increasing off-chain capabilities of the Lightning Network have decreased on-chain transaction bloat. Transaction batching is most effective for entities with a high amount of on-chain transaction outputs, such as miners and exchanges.
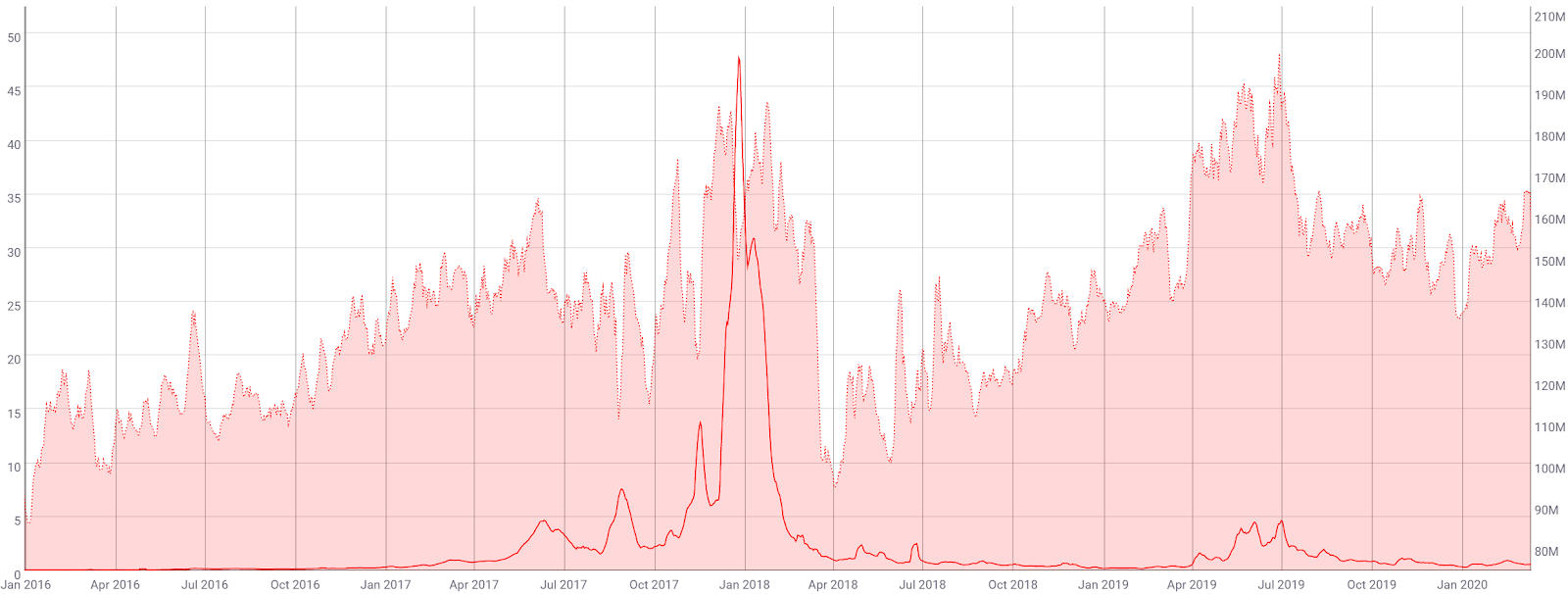
The 30-day Kalichkin network value to on-chain transactions ratio (NVT) increased from 70 to 100 since the beginning of the year, only beginning to decline 95 over the past week (line, chart below). While Kalichkin's NVT does not account for inflation or the use of off-chain transactions, which would decrease the overall NVT ratio, the metric remains in the upper-third of the historic range.
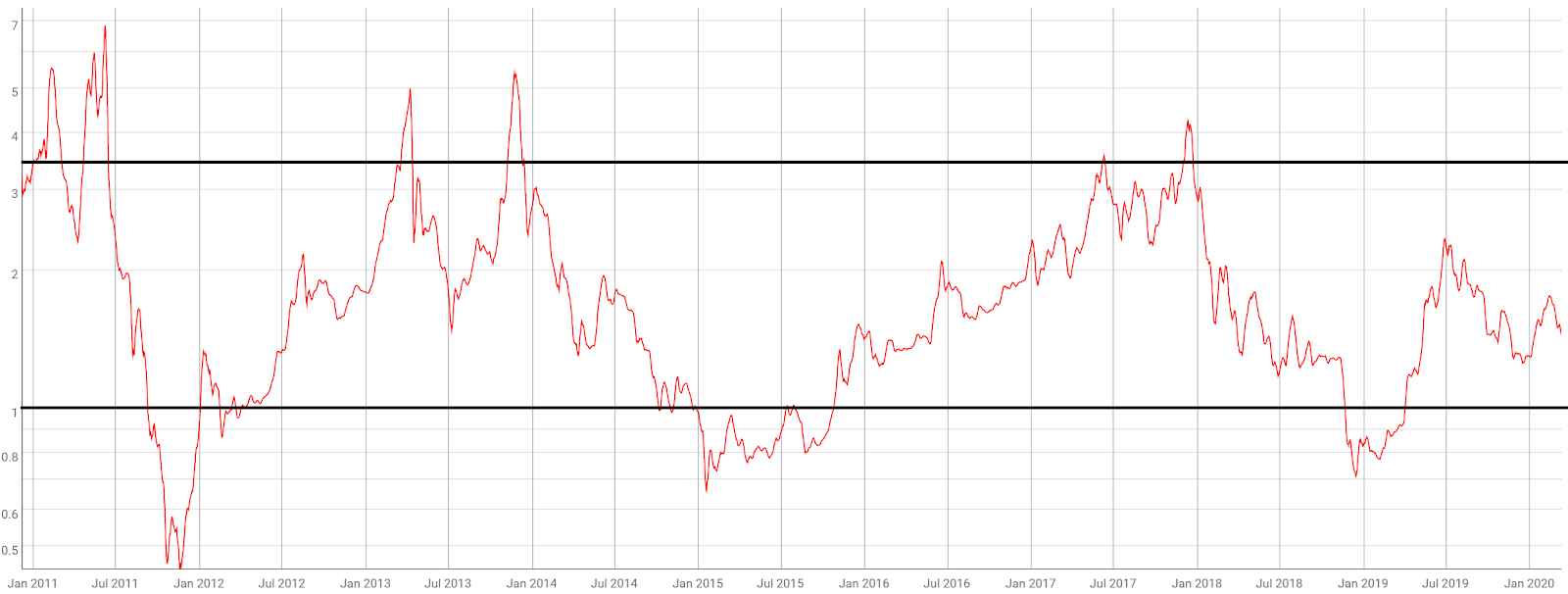
The three previous highs in NVT, in February 2011, October 2014, and October 2018, were all followed by bearish price moves. Based on this metric, the probability for a local top in price will increase if another local NVT high is reached. In December 2018, NVT bottomed out at 46 before a price reversal.
Monthly active addresses (MAAs) have increased to 760,000 over the past three months, marking an eight-month high (fill, chart below). MAAs grew to 850,000 in July 2019, from a 2019 yearly low of 550,000. MAAs have held above 500,000 since October 2016.
Daily active addresses (DAAs) surpassed one million three times in 2019, on June 14th, 26th, and 28th. June 2019 was the first-month that DAAs exceeded one million since February 2018. On December 14th, 2017, DAAs exceeded 1.28 million.
The Bitcoin network has far more active addresses than any other blockchain. A large uptick or sustained increase in DAAs should be seen as a bullish indicator for market prices as it suggests an increase in on-chain BTC demand. As off-chain transaction facilities increase, daily active addresses may stagnate or decline over time.
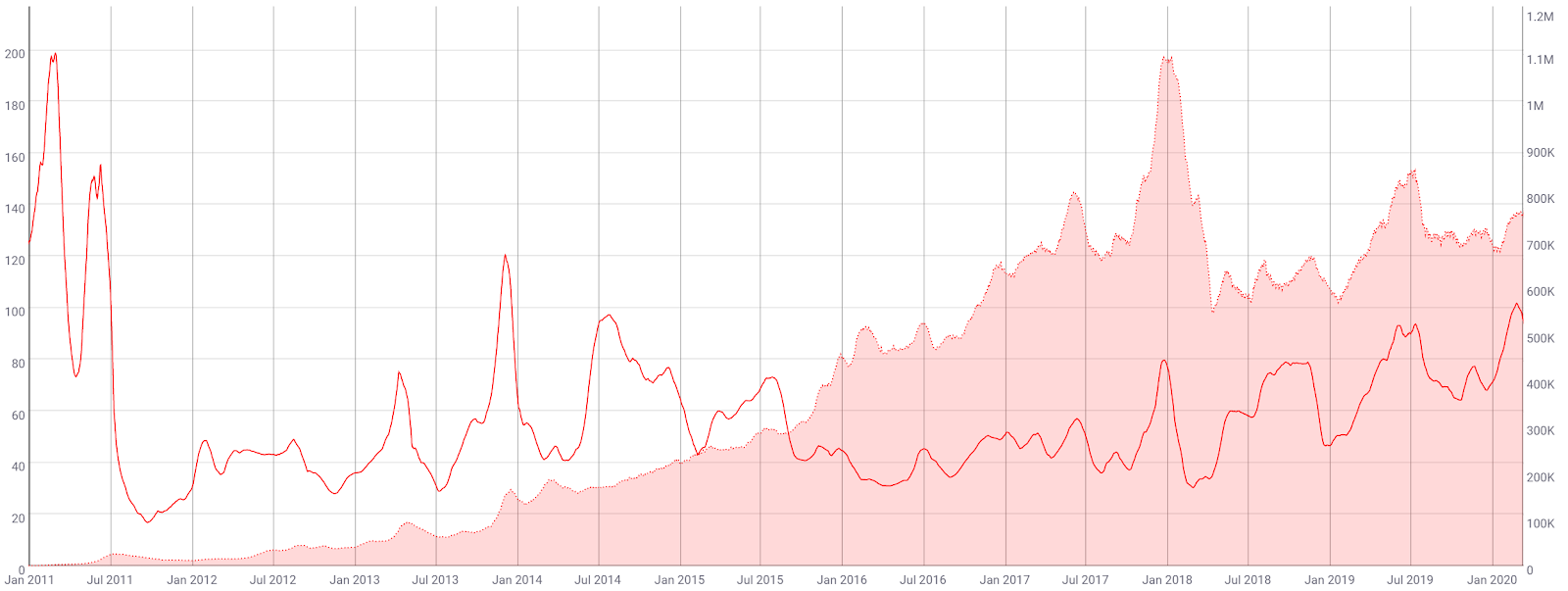
The market cap divided by the realized cap (MVRV) is another crypto-native fundamental metric used to assess overbought or oversold conditions. Realized cap approximates the value paid for all coins in existence by summing the market value of coins at the time they last moved on the blockchain.
Historically, periods of an MVRV less than one have represented oversold conditions, whereas periods of an MVRV greater than 3.5 have represented overbought conditions. Of the MVRV levels above four since January 2013, all three have coincided with record highs in price. Currently, MVRV is 1.46 and falling, holding below the midpoint of the historic range.
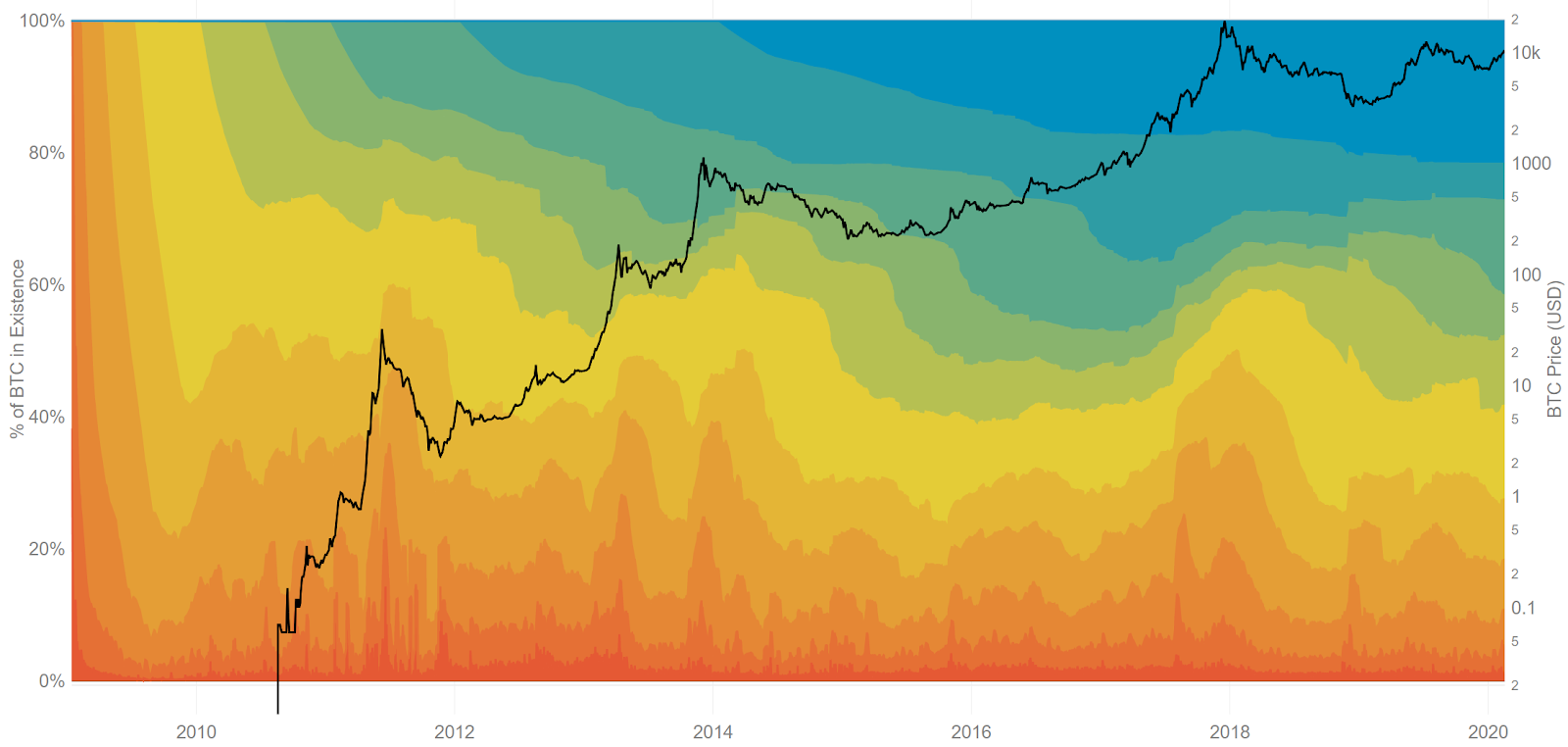
Analyzing the age of unspent transaction outputs (UTXOs), or unspent coins, can also provide some insights into price movements. Spikes in newly moved coins tend to correlate with local tops or bottoms in market values, and can represent euphoria or capitulation. Coins which have not moved recently are represented in cooler colors, whereas coins on the move are represented by warmer colors.
Coins that have not moved in more than five years (dark blue) account for 21.64% of the circulating supply, or around 3.94 million BTC. The six to twelve month age band (yellow), or coins not moved since March 2019 - October 2019, holds the next highest distribution at 14.15%. The one to the three-month band (orange) had gained 5% from April 2019 to June 2019, but has fallen in recent months. Historically, local tops in price have occurred when the one to three-month band, currently 7.48%, has represented more than 15% of all circulating UTXOs.
Turning to developer activity, Bitcoin Core version 0.19.1 was released earlier this month and provided various bug fixes and performance improvements. Future potential protocol improvements in the pipeline include Schnorr signatures, Taproot, and Graftroot.
Schnorr signatures and signature aggregation also bring the potential for storage and bandwidth reduction by at least 25%. Taproot and Graftroot improve upon Merkelized Abstract Syntax Trees (MAST) which offers three benefits; smaller transactions, more privacy, and larger smart contracts.
In September 2019, Pieter Wuille of Blockstream also unveiled plans for miniscript, a simplified way to write Bitcoin code. The current version, Script, is complex and difficult to use for those not intensely familiar with the language.
According to Wuille, miniscript allows a user to write some Bitcoin scripts, “in a structured, composable way that allows various kinds of static analysis, generic signing, and compilation of policies.” Miniscript is in the early stages of development and is currently being tested internally at Blockstream.
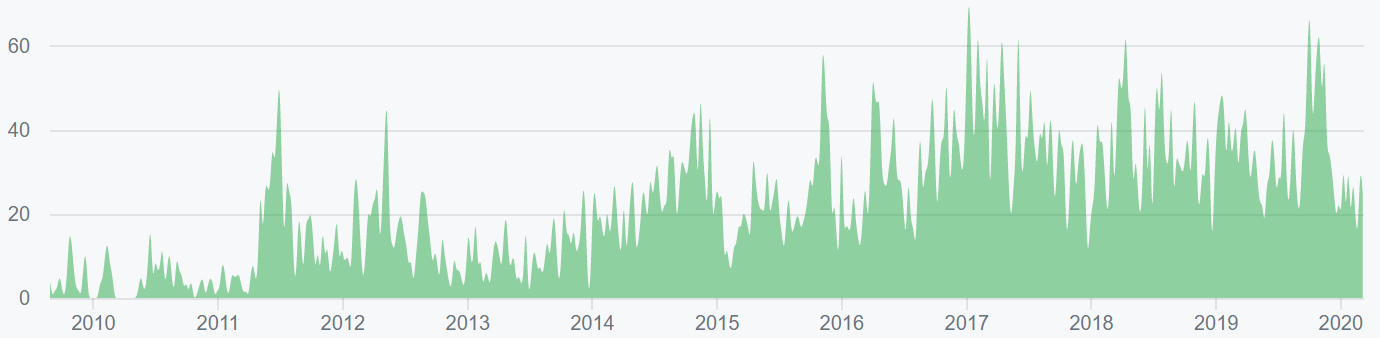
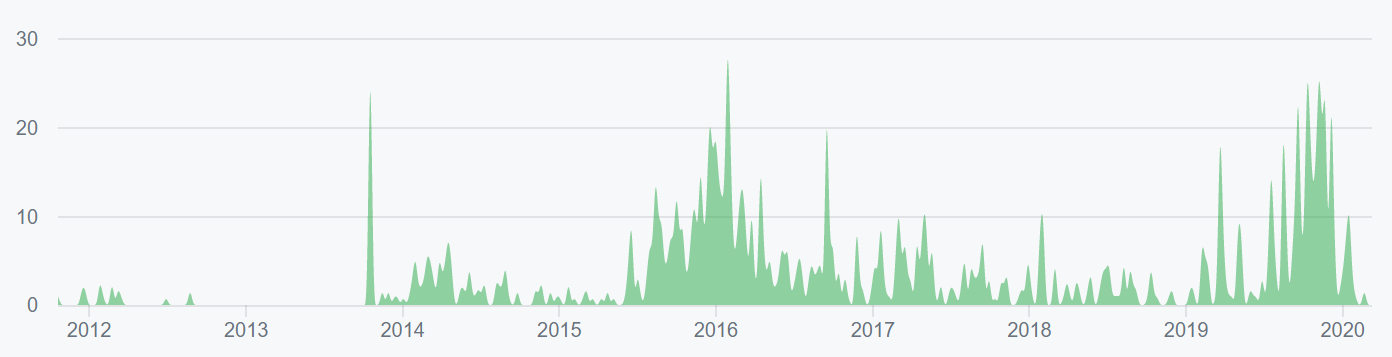
More than 170 developers have contributed nearly 1,700 commits in the past year, mostly on the main Github repo. Most coins use the developer community of GitHub where files are saved in folders called "repositories," or "repos," and changes to these files are recorded with "commits," which save a record of what changes were made, when, and by who. Although commits represent quantity and not necessarily quality, a higher number of commits can signify higher developer activity and interest.
The BTC project on Github has two active repos, “bitcoin” (top chart, shown below) and Bitcoin Improvement Protocols, “BIPs” (bottom chart, shown below).
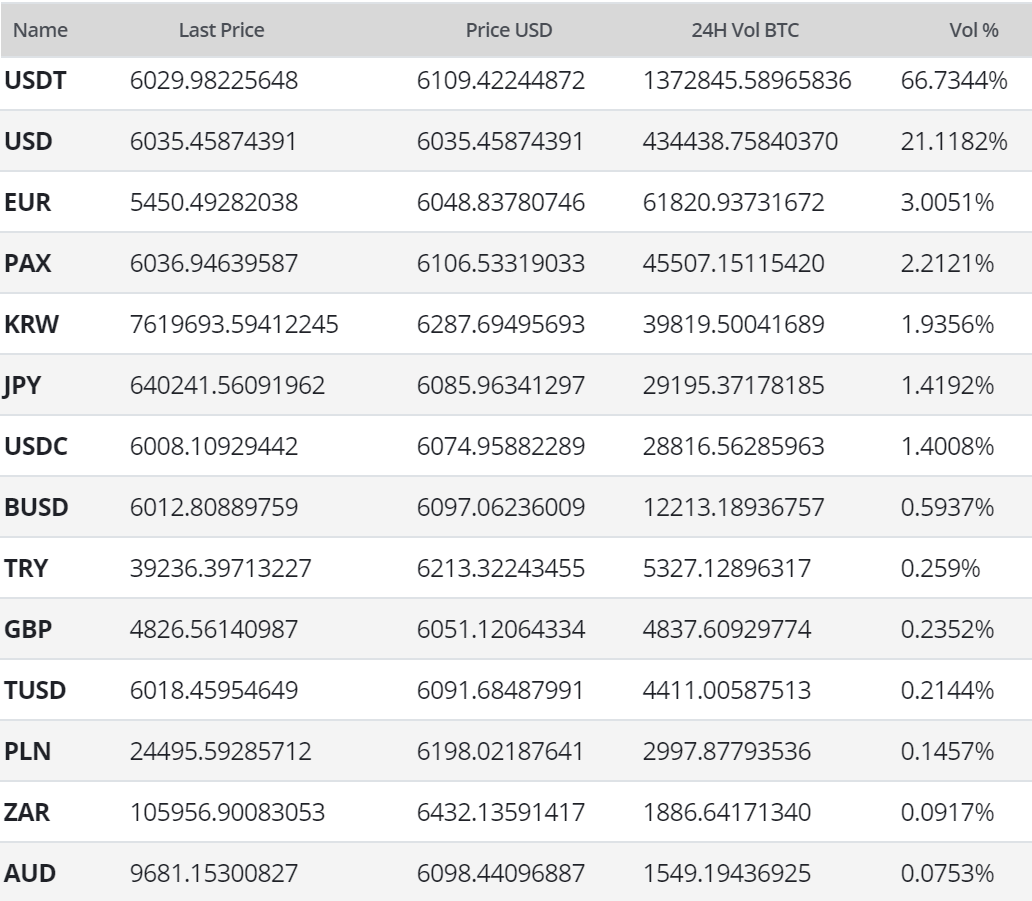
BTC exchange-traded volume over the past 24 hours has been dominated by Tether (USDT) trading, with the United States Dollar (USD) markets representing 21% of the total volume. Tether is a stable coin with a soft peg to the USD. Stablecoins in general currently represent nearly 75% of all reported volume over the past 24 hours.
In 2019, VanEck-SolidX once again withdrew its BTC ETF proposal from the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) review process. All previous ETF proposals thus far have been rejected by the U.S regulator. So far, the SEC has delayed decisions on all active BTC ETF applications. However, there are already several BTC ETNs available, in various jurisdictions across the globe, which are seeing increasing volumes.
In place of a traditional ETF, VanEck-SolidX introduced a limited version of a BTC ETF, made available to qualified institutional buyers. The 144a product currently has US$494,000 under management. The Bakkt physically-settled BTC futures exchange launched in September 2019 and has seen increasing volumes throughout 2019. Bakkt and the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) have also launched a BTC options product.
Global over the counter (OTC) volume, from LocalBitcoins.com, declined from late 2017 to mid 2019, and then declined again from mid 2019 to early 2020. Global notional volume has held near or above US$50 million since the beginning of the year. In May 2019, LocalBitcoins discontinued servicing Iran, likely as a result of U.S sanctions and in June 2019, the option to pay for BTC in person with cash was disabled.
Latin America (brown) holds the highest percentage of total notional volume, followed by Eastern Europe (orange). The Middle East (yellow) and the Australia/New Zealand regions (grey) hold the lowest notional volume, both posted less than US$700,000 in trade volume over the past week. Notional volumes for Venezuela and Columbia stand at US$4.34 million and US$2.56 million, respectively. Venezuela’s central bank also announced plans to hold BTC within its reserve system.
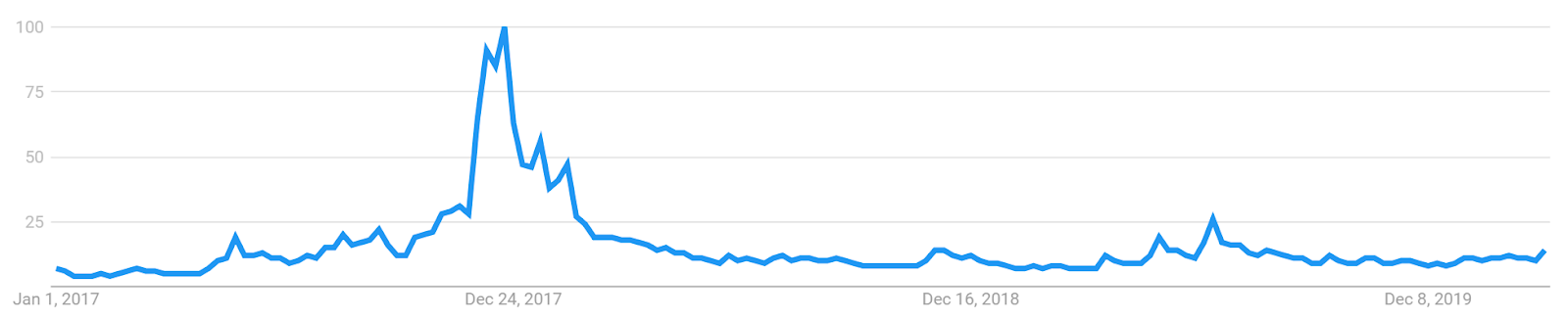
Worldwide Google Trends data for the term "bitcoin" increased dramatically from March to June 2019, marking a new yearly high. Since June, search interest has dropped but has begun to increase slightly again in recent weeks.
The previous increase in search traffic has likely been related to both the sharp increase in price in Q2 as well as mentions from several prominent U.S government officials, including the President of the United States. Throughout the course of 2018, “bitcoin” related searches declined dramatically. Despite the declining interest, the search “what is bitcoin” was the most popular “what is” Google search of 2018.
A slow rise in searches for "bitcoin" preceded the bull run in Q4 2017, likely signaling a large swath of new market participants at that time. However, a 2015 study found a strong correlation between google trends data and BTC price whereas a 2017 study concluded that when U.S. Google "bitcoin" searches increased dramatically, BTC price dropped.
Technical Analysis
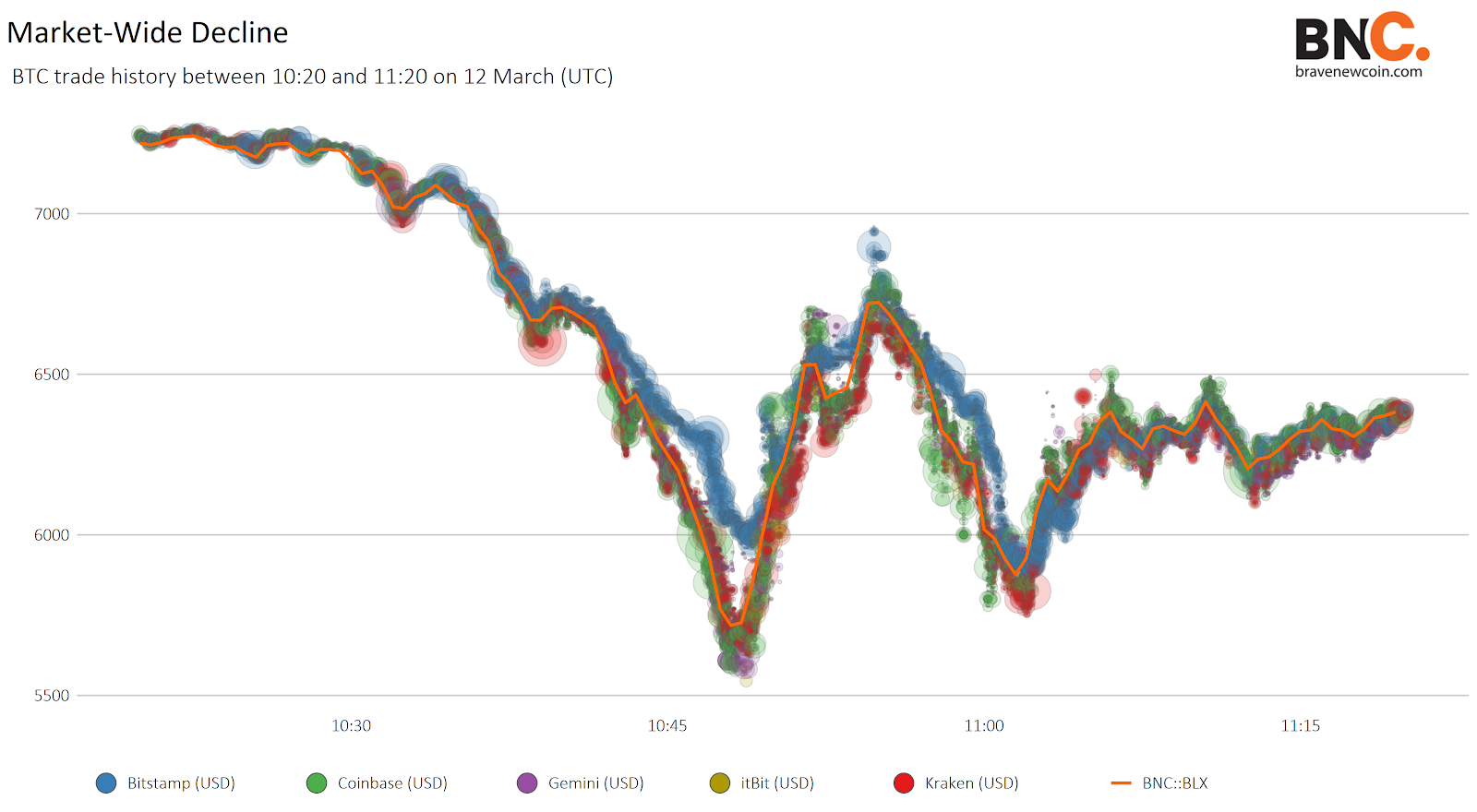
The ~30% decline today saw large and continued market-wide selling across all exchanges. Crypto markets also became increasingly correlated with global legacy markets, which saw the largest daily declines in over 30 years. Oil prices have also declined over 40% in the past month due to the increasing production supply from Russia and Saudi Arabia. Additionally, as Covid-19 is finally being recognized as a global pandemic, commerce and entertainment around the world has come to a halt.
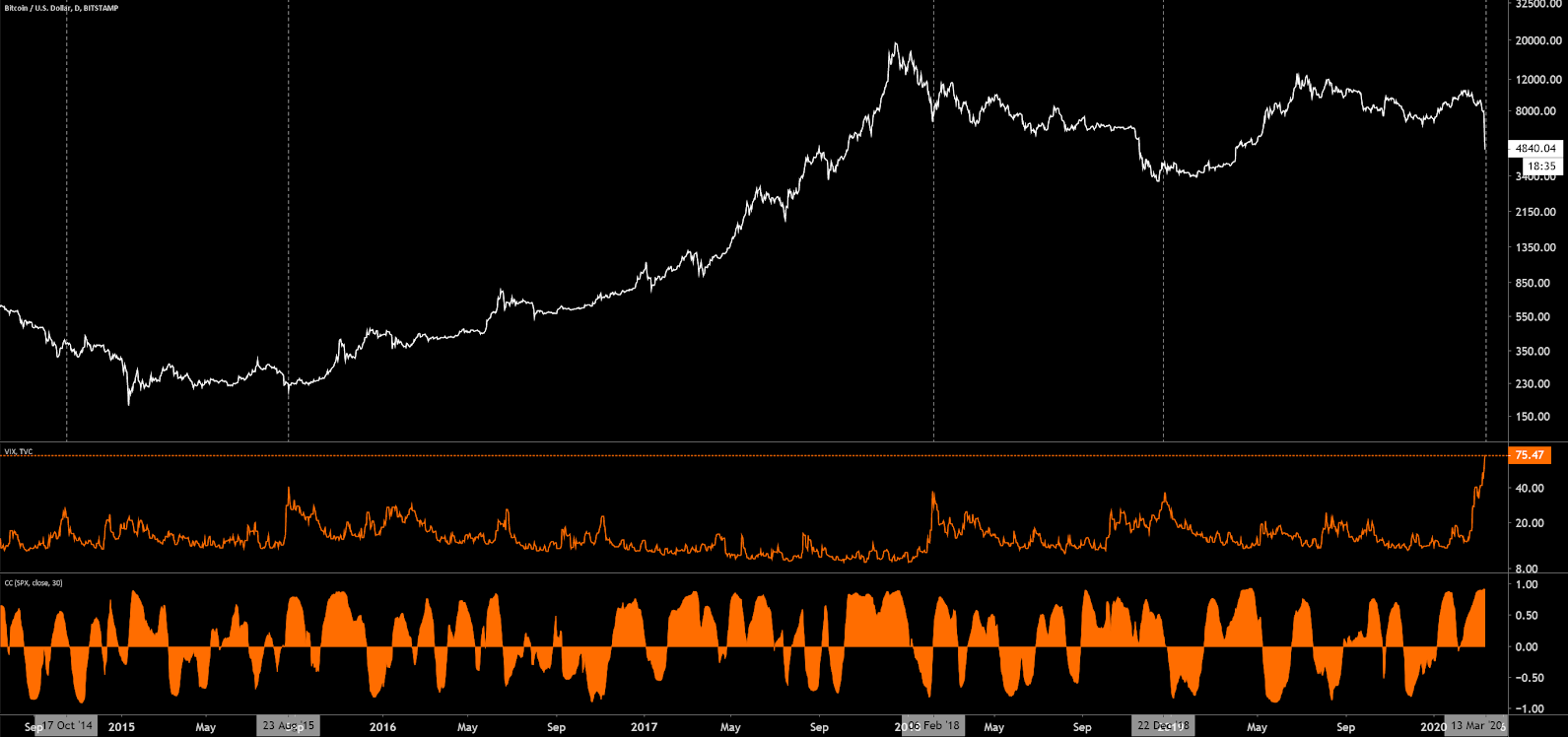
Since October 2014, spikes in the Chicago Board Options Exchange's CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) have represented local lows in BTC price. VIX, or the ‘fear index’, is currently the highest level since the 2008 financial crisis when the metric peaked at 90. The U.S S&P 500 Index has had a near 100% correlation with BTC over the past week.
Conclusion
Bitcoin Proof-of-Work mining will be under severe pressure as Bitcoin continues to nosedive. As prices decline sharply, more and more miners will become unprofitable, and may turn off their hardware. This would result in increased network block times until the next difficulty adjustment.
In the near term, on-chain metrics are unlikely to have a substantial impact on any price recovery. Historically, legacy markets will also need to stabilize in order for buyers to return to the crypto market. Despite the popular belief that Bitcoin will act as a safe-haven store-of-value, exchange price action over the past week has shown the complete opposite. In the months to come, Bitcoin may recover swiftly as quantitative easing and central bank money printing surge to unparalleled levels.
OhNoCrypto
via https://www.ohnocrypto.com
Josh Olszewicz, Khareem Sudlow
